Body Forms
There are three body forms of sponges...
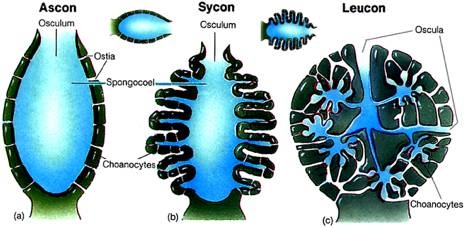
Ascon: the simplest and least common body form of sponges. Shaped like a vase.
Sycon: with a sycon body form, the wall of the sponge is folded. Choanocytes are found in the radial canal.
Leucon: the most complex body form. Unlike the other two body forms, it lacks a spongocoel. A leucon body form can have more than one osculum.
Ascon: the simplest and least common body form of sponges. Shaped like a vase.
Sycon: with a sycon body form, the wall of the sponge is folded. Choanocytes are found in the radial canal.
Leucon: the most complex body form. Unlike the other two body forms, it lacks a spongocoel. A leucon body form can have more than one osculum.
Anatomy & Classes
The phylum porifera contains three major classes...
Calcarea... calcareous sponges: calcareans' skeletal structures are composed of spicules, which are made of calcium carbonate. Each spicule contains three or four rays. Calcarean sponges can be any of the three body forms. All calcarean sponges are found in the ocean.
Hexactinellida... glass sponges: hexactinellida sponges have a skeletal structure that contains spicules that are made of silica. Every spicule contains six rays. Hexactinellida sponges can either be sycon or leucon. They are found in oceans of the West Indies and eastern Pacific.
Demospongiae... freshwater and bath sponges: the skeletal structure of a demospongiae can either be made of spicules made of silica and/or spongin. Demospongiae all have a leucon body form. Some demospongiaes can be found in the ocean, but most are found in freshwater.
Calcarea... calcareous sponges: calcareans' skeletal structures are composed of spicules, which are made of calcium carbonate. Each spicule contains three or four rays. Calcarean sponges can be any of the three body forms. All calcarean sponges are found in the ocean.
Hexactinellida... glass sponges: hexactinellida sponges have a skeletal structure that contains spicules that are made of silica. Every spicule contains six rays. Hexactinellida sponges can either be sycon or leucon. They are found in oceans of the West Indies and eastern Pacific.
Demospongiae... freshwater and bath sponges: the skeletal structure of a demospongiae can either be made of spicules made of silica and/or spongin. Demospongiae all have a leucon body form. Some demospongiaes can be found in the ocean, but most are found in freshwater.
Digestion
Sponges, like cnidarians, don't actively hunt for food. Instead, they use a process called filter feeding. All three body forms and all three classes of sponges share the same process of acquiring food. There are four stages of filter feeding...
1. Water enters the pore of a sponge.
2. The flagella create a current in the canals.
3. Eventually, food particles in the water will be caught on the collar of a choanocyte.
4. Excess water is pushed out through the osculum.
1. Water enters the pore of a sponge.
2. The flagella create a current in the canals.
3. Eventually, food particles in the water will be caught on the collar of a choanocyte.
4. Excess water is pushed out through the osculum.
Representative organism: callyspongia Vaginalis

- Scientific name: Callyspongia vaginalis
- Common name: tube sponge
- Class: demospongiae
- Color varies from lavender to brown-gray to green-gray, sometimes light tan

- Eats bits and pieces from dead fish
- Vent of a tube sponge's tubes are wide and thin
- The tubes can be as high as 25 cm and can be up to 5 cm in diameter
- The vents can be up to 2.5 cm in diameter
- Usually found in shallow and mid-range reefs
- Common in South Florida, the Bahamas, and the Caribbean
Source for poriferan info:
http://www.oceanicresearch.org/education/wonders/sponges.html
Source for tube sponge:http://species-identification.org/species.php?species_group=caribbean_diving_guide&menuentry=soorten&id=443&tab=beschrijving
Similarities with Cnidarians
- The polyp form of cnidarians, like sponges, are sessile
- Cnidarians and poriferans are diploblastic
- Sponges and polyps are capable of sexual or asexual reproduction
- Sponges and polyps float around at a very young age before they attach themselves to an object
- Cnidarians and poriferans are carnivorous
- Cnidarians and poriferans lack true tissue or organs
- Cnidarians and poriferans are invertebrates